HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statins) Custom Development
BOC Sciences can provide development and manufacturing services for statin Featured APIs. Statins, also known as hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors, are the most widely used and effective lipid-lowering drugs in the world. With the increase of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases year by year, statins have become an indispensable part of the treatment and prevention of such diseases. Recently, the therapeutic use of statins has been increasingly recognized recently, so its economic impact on the pharmaceutical market is huge. We can provide you with the synthesis and industrial production of statin specialty APIs and key intermediates, and accelerate product launch, greatly improving your competitiveness in the industry.
What are HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors?
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors are drugs that lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. HMG-CoA reductase is involved in the production of cholesterol in the liver. By inhibiting this enzyme, the amount of cholesterol produced in the body can be reduced, thereby lowering blood cholesterol levels. Among them, statins are the most commonly used HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors.
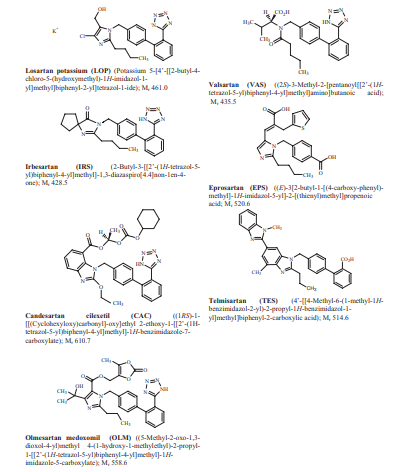
 Fig. 1. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors from the endophytic fungus Colletotrichum capsica (Natural Product Research. 2023, 1478-6419).
Fig. 1. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors from the endophytic fungus Colletotrichum capsica (Natural Product Research. 2023, 1478-6419).
Statins inhibit the rate-limiting enzyme in the process of cholesterol synthesis in the body, while promoting the metabolism of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C). The molecular structures of several common statins are shown in Fig 1. According to the chemical structure, the mechanism of action of statins can be divided into three parts:
- The first part is an analog of the target enzyme substrate (HMGCoA).
- The second part is covalent to the substrate analog. The complex hydrophobic ring structure that connects and participates in the binding of statins to reductases.
- The third part is the side groups on the rings, which define the solubility properties of the drugs as well as many of their pharmacokinetic properties.
Structure Activity Relationship
1) 3,5-dihydroxycarboxylic acid is a necessary structure to produce enzyme inhibitory activity. Compounds containing lactone must be hydrolyzed to take effect and can be regarded as prodrugs. And the absolute configuration of 3,5-dihydroxy plays a crucial role in producing drug efficacy.
2) The decalin ring in the ring A part is necessary to bind to the active site of the enzyme, and if substituted with a cyclohexyl group, the activity is reduced by 10,000 times. W, X, Y in the ring B part can be carbon or nitrogen, n is 0 or 1
Classification of Statins
1) Natural medicines: Commonly used medicines include lovastatin. Lovastatin is a natural HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. However, due to the lactone structure in the molecule, it is ineffective in vitro. It requires the hydroxylactone structure in the molecule to be hydrolyzed into 3,5-dihydroxyvaleric acid after entering the human body to show activity. Lovastatin has 8 chiral centers. If the configuration of the chiral centers is changed, the activity will be reduced. Lovastatin can competitively inhibit HMG-GoA reductase with high selectivity, significantly reduce LDL levels, and increase HDL levels in plasma.
2) Semi-synthetic modified drugs: Commonly used drugs include simvastatin and pravastatin. Simvastatin is a drug modified on the side chain of the decalin ring of lovastatin. Compared with lovastatin, it only has one more methyl substituent on the side chain of the decalin ring, and the lipophilicity and activity are slightly improved.
3) Fully synthetic drugs: Commonly used drugs include fluvastatin, atorvastatin, and rosuvastatin. In the structure of fluvastatin, an indole ring is used to replace the bicyclic ring in the lovastatin molecule, and the lactone ring is opened to form a salt with sodium to obtain fluvastatin sodium. Fluvastatin has good water solubility, rapid and complete oral absorption, and high protein binding rate. In the structure of atorvastatin, a pyrrole ring is used to replace the bicyclic ring in the lovastatin molecule, with a ring-opened dihydroxyvaleric acid side chain. The bicyclic part of rosuvastatin molecule is changed into a multi-substituted pyrimidine ring. This product is clinically used for primary hypercholesterolemia or mixed dyslipidemia that cannot be properly controlled by diet control and other non-drug treatments.
Our Statin Development Services
BOC Sciences is a leading supplier of research chemicals and pharmaceutical intermediates, including statins. We provide a series of services related to statin drug development, including custom synthesis of statin drugs and their intermediates, production process development and optimization, characterization and purity analysis services, and formulation development. Our statin development services include but are not limited to the following:
Catalytic Synthesis of Statins
We employ green and sustainable biocatalytic methods to prepare statins and are able to implement different biocatalytic pathways on an industrial scale for the stereoselective preparation of side chains (with stereocenters) of superstatins. The types of biocatalysts we use include nitrilases, ketoreductases and aldolases, etc.
Fermentative Synthesis of Statins
In addition to biocatalytic synthesis, we can also use microbial fermentation to prepare fermentation-derived statins. The microorganisms we use are mainly divided into two types of mold groups: Aspergillus and Penicillium, and the methods involved are submerged fermentation and solid-state fermentation.
Consistency Evaluation of Statins
Our consistency evaluation service mainly includes pharmaceutical equivalence and bioequivalence evaluation. The former is to evaluate whether the active ingredients, dosage, route of administration, and dosage form of the drug are consistent with the original drug and meet the drug quality standards. The latter verify that the absorption and metabolism of generic drug preparations in the body are consistent with the original drug.
BOC Sciences has extensive capabilities in the development of statins and can provide customized solutions to meet the specific needs of clients in the pharmaceutical industry. We can provide statin drug preclinical and clinical research contract research services according to customer project needs. Regulatory and registration support for statin drug development in different regions is also available at BOC Sciences. If you are interested in our custom development services, please contact us immediately.
Case Study
The purpose of this case study is to highlight the custom development services provided by BOC Sciences for the synthesis of lovastatin and related impurities. As a leading provider of custom synthesis solutions to pharmaceutical companies, research institutions and academic laboratories, our experienced team of chemists and scientists can design and execute custom synthesis projects to meet our customers' specific needs.

BOC Sciences offers comprehensive custom synthesis services for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, including lovastatin and related impurities. Our team of experts can design and optimize synthetic routes to produce these compounds, taking into account factors such as yield, purity and scalability. Our state-of-the-art equipment and facilities allow us to perform complex chemical reactions and purifications with high precision and efficiency.
FAQ
1. What prodrug is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor?
Simvastatin is a prodrug that is converted in the liver to its active form, which is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. It is often used to help lower cholesterol levels in the blood, specifically low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Simvastatin works by inhibiting the enzyme in the liver responsible for producing cholesterol, ultimately reducing the amount of cholesterol circulating in the blood.
2. What happens if HMG-CoA reductase is inhibited?
If HMG-CoA reductase is inhibited, the synthesis of cholesterol in the body will be reduced. This enzyme is a key regulator of cholesterol production, so inhibition of it can reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. This is beneficial for people with high cholesterol levels because it can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke.
Reference
- Lu, Y. et al. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor from the endophytic fungus Colletotrichum Capsici. Natural Product Research. 2023, 1478-6419.